 |
|

NLI-Z39.50 tour start |
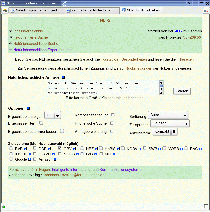
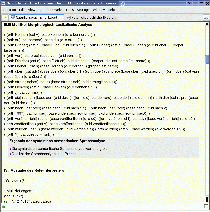
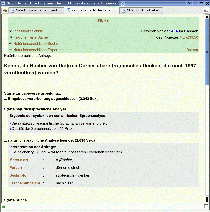
This interface allows the user - without knowing technical details - to submit a natural language to the NLI. All search options have been assigned default values. Moreover, suitable target systems are selected by the Broker. In addition, the query history is displayed and updated during the search process.

|
| Fig. 2: Graphical User Interface of the NLI-Z39.50. |
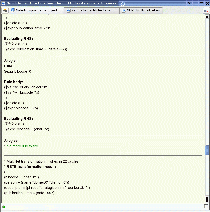
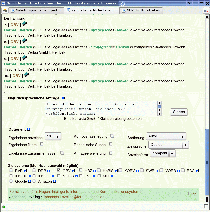
In expert mode of the NLI-Z39.50, the user has control over a variety of parameters directly influencing the search results. Furthermore, target systems can be selected from a list of available systems for a parallel search.
 |
| Fig. 3: Graphical User Interface of the NLI-Z39.50 in expert mode. |
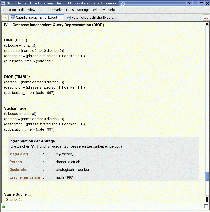
Because the screenshots are from the original German version of the NLI-Z39.50 and have not been translated, the following sections describe and translate all elements of the graphical user interface of the NLI-Z39.50. The graphical user interface of the NLI-Z39.50 contains the following elements:
| 1. | Natural
language query (Natürlichsprachliche
Anfrage) This text field contains the user's natural lamnguage query. After selecting target systems and options for a search, the button Starten (Start search) will initiate the search for bibliographic references. |
||||||||||||||||||
| 2. | Query
history (Anfrageverlauf) The previously submitted queries of a user are displayed for a successive refinement of a query. |
||||||||||||||||||
| 3. | Options
(Optionen) The following options are available in the NLI-Z39.50:
|
||||||||||||||||||
| 4. | Target
systems (Zielsysteme) This set of checkboxes provides the user with a means to select target systems for a query, which can then be processed in parallel. Target systems include, for example, the Library of Congress, most major library catalogs in German-speaking countries, and the library of Die Deutsche Bibliothek in Frankfurt / Leipzig. |
 |
| <
|
<
|
 |
|
 |
| |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 ,
,
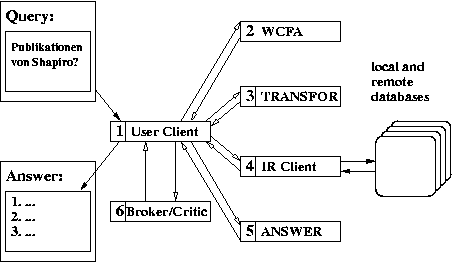 |
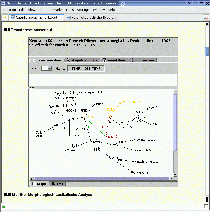
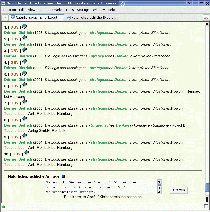
| Fig. 1: System architecture of the NLI-Z39.50. |
| University of Hagen, IICS, [email protected] |